Introduction
Learning personal productivity is a must to be successful in any sector of this world, full of demands and distractions. In general, any professional or student, and even experienced data analysts, must have effective time management, work prioritizing, and goal achievement as major skills to be successful. The other important components of personal productivity are building effective workflows, developing self-discipline, and creating a work-life balance that supports long-term growth and fulfillment—not just checking boxes off a to-do list.
The challenge in today’s fast-paced workplace isn’t just a matter of keeping busy but working more effectively. Personal productivity means balancing your objectives with your input while juggling conflicting priorities and interruptions. It involves knowing how to delegate well, using time management strategies to allow for unbroken periods of concentration, and task-prioritizing tactics that ensure your energy is directed to the most productive tasks. While these are general rules, they can be tailored to fit specific jobs and tasks.
For data analysts, personal productivity takes on an added dimension. The nature of the job is an exploration of datasets, reporting, and conclusions—all of which demand not only focus but also a systematic way of managing tasks and efficiency tools. It involves a balance between the inventiveness required in visualization and narrative and the fastidious attention to detail that goes into data cleansing and validation. Productivity is an important skill for staying inventive and competitive in the field, as technologies and approaches do change, hence requiring proactive learning.
This article provides hands-on tactics that will help you realize your greatest potential and bring outstanding results, based on the foundation of time management, goal setting, and performance monitoring. These strategies will help data analysts and professionals improve their processes, achieve better results, and create a viable career path to long-term success and fulfillment.
The Foundations of Personal Productivity
1. Time Management
Time is a finite resource, and managing it effectively is the cornerstone of personal productivity. For data analysts, this involves structuring your day to balance deep-focus tasks, like coding or data visualization, with lighter activities such as team meetings or email correspondence. Techniques like the Pomodoro Technique or time-blocking can help allocate dedicated time slots for specific tasks, minimizing distractions and maximizing efficiency.

2. Goal Setting
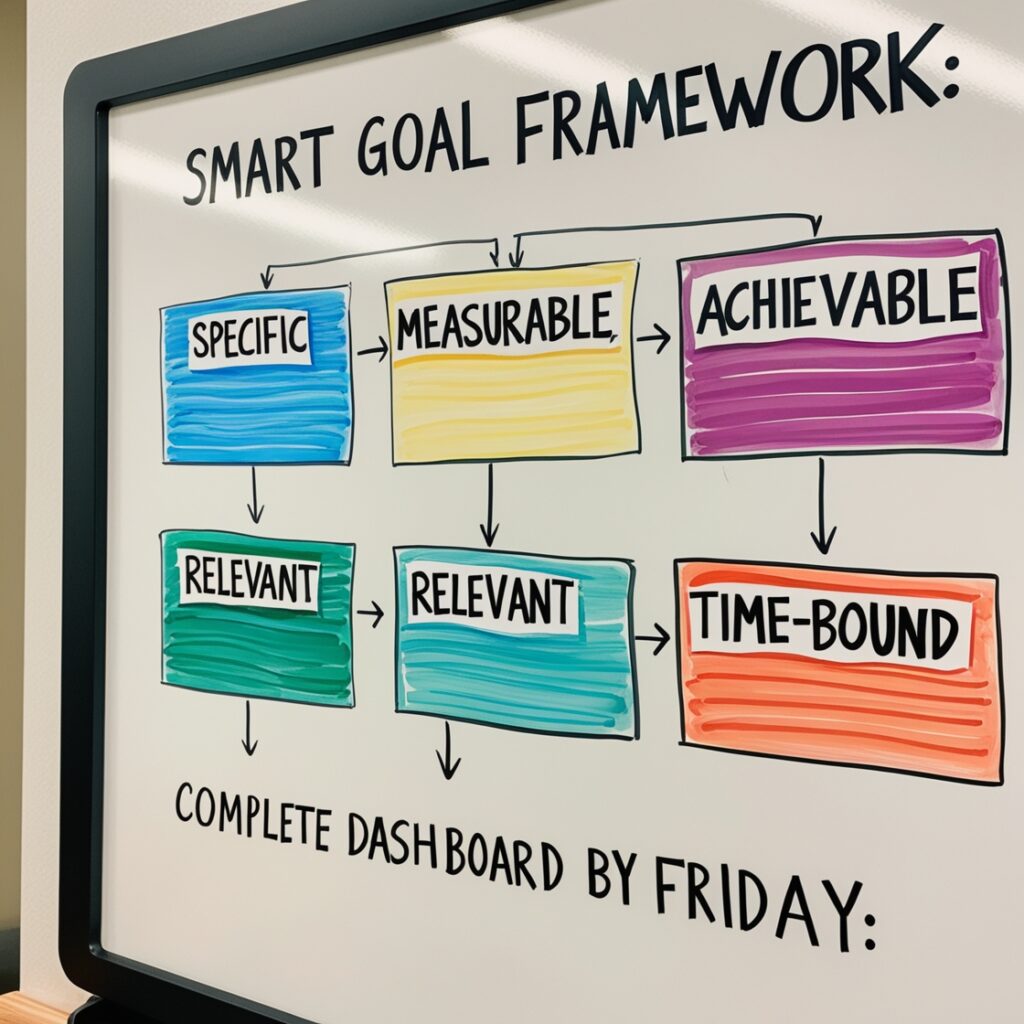
Clear and actionable goals provide direction and purpose. As a data analyst, setting goals for both short-term projects (e.g., completing a dashboard by Friday) and long-term objectives (e.g., mastering a new tool like Power BI) can help you stay focused. Utilizing frameworks like SMART goals ensures that your objectives are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
3. Task Prioritization
Prioritizing tasks is essential to avoid feeling overwhelmed. Tools like the Eisenhower Matrix categorizing tasks by urgency and importance can guide you in focusing on high-impact activities. For instance, prioritizing data validation over formatting ensures that your analysis remains accurate and insightful.

Leveraging Tools and Habits for Maximum Efficiency
1. Productivity Tools
In the digital age, leveraging productivity tools can streamline workflows. As a data analyst, tools like Jira for task tracking, Notion for project organization, or Slack for team communication can save precious time. Combining these with data-specific platforms such as Tableau or SQL clients ensures that your technical and organizational needs are met seamlessly.

2. Daily Routines
Establishing a structured daily routine can significantly enhance focus and self-discipline. Starting your day with a clear agenda, allocating time for breaks, and reviewing completed tasks can help maintain momentum. Incorporating mindfulness practices like meditation can boost mental clarity, reduce stress, and enhance overall productivity.

3. Performance Tracking
Monitoring your productivity allows for continuous improvement. Tools like Trello, Asana, or even simple spreadsheets can help track progress against your goals. Creating a personal dashboard to monitor metrics such as time spent on specific projects, number of completed analyses, or learning milestones can provide valuable insights for data analysts.

The Role of Data Analytics in Personal Productivity
Data analytics isn’t just a career; it’s a mindset. Applying data-driven principles to personal productivity can yield transformative results. For example:
- Tracking Performance Metrics: Use productivity apps or Excel to analyze how you spend your time and identify areas for improvement.
- Experimenting with Techniques: Treat productivity strategies like A/B tests—try different approaches, measure their effectiveness, and refine them accordingly.
- Leveraging Insights: Analyze patterns in your workflow to uncover bottlenecks or inefficiencies, allowing for informed adjustments.
Conclusion
Personal productivity is a continuous learning and adaptation journey. For data analysts, it means combining technical skills with effective time management, goal setting, and workflow optimization. Combining these with the integration of useful productivity tools, fostering self-discipline, and tapping into data-driven insights will help one protect against that thin line between professional excellence and personal well-being.
This balance doesn’t happen overnight. It requires dedication to building habits that concentrate on efficiency and intentionality in your actions day by day. For example, using digital tools such as task managers and time trackers could give clarity on your progress, while reflecting on your achievements will help you stay aligned with your greater goals. Small, consistent adjustments to your routine will, over time, make large improvements possible for continued success.

The key to unlocking your productivity lies in taking deliberate action and regularly reviewing your progress. It includes being open to change, learning from setbacks, and always seeking improvement. From analyzing big, complicated datasets to juggling and managing competing priorities, personal productivity is about empowering yourself to work smarter, achieve more, and face the challenges in your field with confidence.
After all, personal productivity is not a professional skill; it’s a life skill. It is making the most of every moment, be it at work or in your personal life, and driving forward with purpose and clarity. As you start to implement these principles into your career as a data analyst—or, frankly, in whatever other role you identify with—you’ll notice that you don’t just excel in your professional pursuits; you design a life that’s highly fulfilling and balanced.


