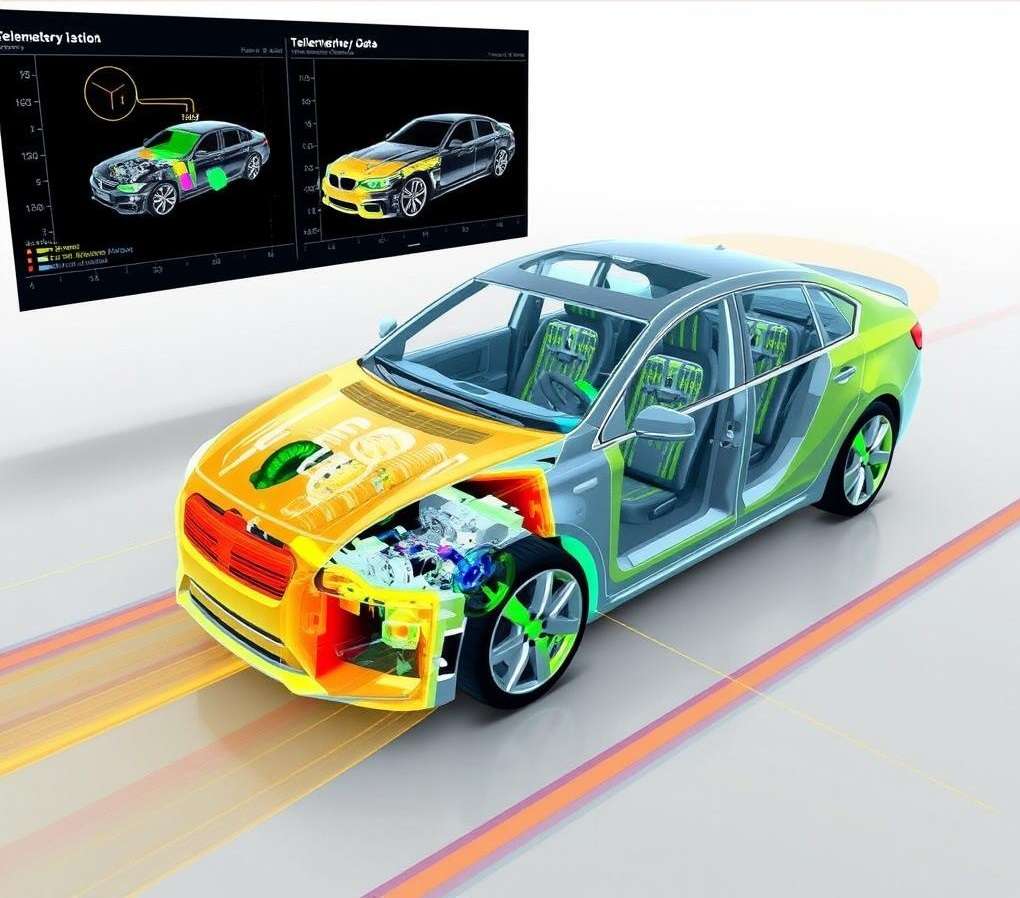
Introduction
Data Analytics has become a keystone of innovation in the quickly changing automotive sector, radically changing the way cars are created, maintained, and constructed. Manufacturers may obtain deeper insights into each phase of the vehicle lifecycle, from conceptual design to after-sale maintenance, by integrating advanced Data Analytics approaches. Utilizing Telemetry Data, a vital resource that offers constant, real-time input on a vehicle’s performance, safety factors, and operating efficiency, lies at the heart of these developments.

Modern cars run on Telemetry Data, which is more than just a set of numbers. It gathers vital Sensor Data from a variety of parts, such as the engine, transmission, brakes, and even the surroundings. Because of the constant monitoring and analysis of this data, automakers can optimize vehicle designs and identify possible problems before they arise. For example, engineers might find trends that can point to the need for design changes that would result in more ecologically friendly and fuel-efficient cars by examining Telemetry Data on engine temperatures, fuel consumption, and exhaust emissions.
Since Telemetry Data is real-time, it presents never-before-seen possibilities for Remote Data Collection and Real-Time Monitoring, both of which are crucial for improving the dependability and safety of vehicles. Telemetry Data enables smooth communication between the vehicle and external systems, enabling services like Fleet Management and Predictive Maintenance, as vehicles become more and more linked through IoT Integration. These developments enhance the overall driving experience by guaranteeing that cars are constantly in top condition and saving operating costs by limiting downtime and preventing breakdowns.

Furthermore, the knowledge obtained from Telemetry Data is essential for improving Vehicle Diagnostics. Manufacturers can turn raw Telemetry Data into usable intelligence by utilizing Data Analytics and seeing trends and anomalies that might point to underlying problems. This proactive approach to diagnostics improves the longevity and performance of the vehicle while also cutting down on the time and expense involved with conventional maintenance procedures.
One cannot stress how crucial it is to comprehend and use Telemetry Data properly as automobile technology develops. For automakers, it means maintaining a lead in a cutthroat industry by producing cars that are safe, effective, and high-performing. It means having the resources to innovate and push the limits of what is feasible in the manufacturing and design of vehicles for engineers. Additionally, it entails customers reaping the rewards of a more dependable, customized, and linked driving experience.
What is Telemetry Data?
The term “telemetry data” describes the automated communication method in which information is sent to a central system for processing, monitoring, and analysis from a variety of sensors that are mounted in a car. These sensors record data in real-time on important parameters such as engine performance, speed, fuel efficiency, and environmental conditions. After that, data analysts use sophisticated data analytics tools to examine the data to find patterns, trends, and any problems that could lead to better vehicle designs, more efficient maintenance plans made possible by predictive maintenance, and improved overall performance and safety of the vehicles. Manufacturers may create automobiles that are safer, more dependable, and more efficient by utilizing Telemetry Data to inform their decisions.
The Role of Telemetry Data in Modern Vehicles
Telemetry Data is the foundation of many innovative automotive advancements, providing priceless insights that promote gains in vehicle efficiency, safety, and performance. In the automobile sector, this data is a basic part of Data Analytics, enabling the gathering and analysis of crucial information that influences the functioning and design of modern vehicles.

Here are some important domains where Telemetry Data is indispensable:
1. Gathering Sensor Information
- Telemetry Data allows for the continuous collection of Sensor Data from various vehicle components, such as the engine, gearbox, brakes, and environmental sensors.
- Understanding how a car behaves in various driving situations—such as changing speeds, different road types, and varied weather conditions—requires access to this Sensor Data.
- Engineers can improve the overall functionality and design of vehicles, as well as their performance, safety, and longevity, by using this data to inform their decision-making.
2. Improving Vehicle Diagnostics
- In the field of Vehicle Diagnostics, Telemetry Data is invaluable, as it enables real-time monitoring to identify potential problems before they become serious.
- For example, Telemetry Data can notify engineers in real-time when anomalous engine temperatures, irregular fuel use, or unusual braking patterns occur.
- By addressing problems early on, this proactive approach to Vehicle Diagnostics not only saves on expensive repairs but also increases the lifespan of automobiles.
3. Real-Time Tracking to Enhance Fleet Management
- Telemetry Data is vital for more than just tracking individual vehicles; it is also essential for fleet-wide Real-Time Monitoring.
- This capability provides a comprehensive picture of vehicle health, performance, and usage patterns by enabling manufacturers and fleet operators to monitor multiple vehicles simultaneously.
- Fleet Management depends on Real-Time Monitoring enabled by Telemetry Data, where optimizing vehicle usage and maintenance schedules can lead to significant cost savings.
- Fleet managers can reduce overall expenses and increase operational efficiency by using data to inform decisions about driver behavior, vehicle wear and tear, and fuel efficiency.
4. Aiding in Predictive Maintenance
- By continuously providing feedback on Performance Metrics that are essential to vehicle health, Telemetry Data supports Predictive Maintenance.
- This data-driven approach allows manufacturers and fleet operators to predict when a vehicle will need repair, minimizing downtime and preventing unplanned breakdowns.
- Utilizing Telemetry Data for Predictive Maintenance keeps vehicles in top condition, extending their lives and increasing reliability.
5. Encouraging Integration of IoT with Autonomous Vehicles
- The automotive sector has benefited from the expanded applications of IoT (Internet of Things) technology through the integration of Telemetry Data.
- IoT Integration enhances connectivity and the overall driving experience by enabling communication between vehicles and other vehicles or with traffic control networks.
- Telemetry Data is crucial for making real-time decisions in the domain of Autonomous Vehicles, providing self-driving systems with the necessary information to navigate safely and effectively.
Telemetry Data is the foundation of contemporary automotive Data Analytics, driving efficiency and innovation in areas such as Fleet Management, Vehicle Diagnostics, and vehicle design. Thanks to its real-time insights, fleet operators and manufacturers can make data-driven, well-informed decisions that improve vehicle longevity, safety, and performance.
Enhancing Vehicle Performance and Safety
Optimizing Vehicle Maintenance and Efficiency
Telemetry Data plays a pivotal role in optimizing vehicle maintenance and efficiency, offering manufacturers and fleet operators valuable insights that lead to improved performance and reduced operational costs.

1. Predictive Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance is one of the most critical applications of Telemetry Data.
- By continuously monitoring Performance Metrics such as engine temperature, oil pressure, and brake wear, manufacturers and fleet operators can predict when a vehicle is likely to require maintenance.
- This predictive approach helps in reducing downtime, as potential issues can be addressed before they lead to more significant problems.
- Telemetry Data enables a proactive maintenance strategy, ensuring vehicles remain in optimal condition, leading to longer lifespans and better overall performance.
- This approach not only prevents costly repairs but also improves vehicle reliability and customer satisfaction.
2. Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing Emissions
- Telemetry Data is instrumental in improving Fuel Efficiency and reducing vehicle emissions.
- By analyzing Performance Metrics, manufacturers can identify areas where vehicles consume more fuel or produce higher emissions.
- These insights allow for necessary adjustments, such as optimizing engine performance, adjusting driving modes, or refining aerodynamics, to enhance fuel efficiency.
- Telemetry Data also helps in identifying driving behaviors or conditions that contribute to higher fuel consumption, enabling the development of driver training programs or adaptive vehicle technologies.
- This capability is crucial in meeting environmental regulations, as manufacturers strive to reduce the carbon footprint of their vehicles and develop more sustainable transportation solutions.
- Additionally, the data-driven approach to improving fuel efficiency ensures that vehicles are more economical to operate, benefiting both the environment and the end-users.

Telemetry Data is essential for optimizing vehicle maintenance and efficiency through Predictive Maintenance and the enhancement of Fuel Efficiency. By continuously monitoring Performance Metrics, manufacturers and fleet operators can take a proactive approach to maintenance, reducing downtime and extending vehicle lifespans. Furthermore, Telemetry Data enables the development of more sustainable vehicles by reducing emissions and improving fuel economy, aligning with environmental goals and regulations. This data-driven strategy ensures that vehicles are not only reliable and efficient but also contribute to a more sustainable future in transportation.
Conclusion
Telemetry Data is an essential component of contemporary automotive Data Analytics and has a significant impact on the advancement of vehicle performance, maintenance, and design. Telemetry Data is positioned as a fundamental tool for both fleet operators and manufacturers due to its capacity to offer real-time insights into every facet of a vehicle’s functioning, from engine performance to safety systems and maintenance needs.
Telemetry Data will become even more important as the car industry moves closer to a future characterized by greater autonomy and connection. To operate effectively and safely, vehicles are growing more complex, with more sensors and networked systems that depend on Telemetry Data. This data helps to manage and monitor individual cars instantly, but it also makes it possible to gather a tonne of information about entire fleets, which can then be analyzed to identify patterns, anticipate problems, and improve performance overall.

New developments in the automobile sector are being propelled by the incorporation of Telemetry Data with cutting-edge technology like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Autonomous Vehicles. Real-time updates on traffic, vehicle health, and weather forecasts are sent to drivers via IoT Integration, which makes it possible for cars to interact with external systems with ease. The real-time decision-making procedures that enable Autonomous Vehicles to safely and effectively navigate complicated settings depend heavily on Telemetry Data.
The automobile sector may produce future vehicles with hitherto unheard-of levels of sustainability, safety, and efficiency by utilizing Telemetry Data properly. Through the use of data-driven design and maintenance strategies, vehicles are guaranteed to operate in a way that maximizes performance while minimizing their negative effects on the environment. Automobiles that are safer, more dependable, and better equipped to meet the demands of a world that is changing quickly will continue to be developed thanks in large part to the advancement of Telemetry Data. A future where transportation is more connected, intelligent, and sustainable than ever before will be achievable due to manufacturers’ ability to push the envelope in vehicle design through the ongoing evolution and application of Telemetry Data.